jit-spell 
- Description
- Just-in-time spell checking
- Latest
- jit-spell-0.5.tar (.sig), 2025-Oct-12, 50.0 KiB
- Maintainer
- Augusto Stoffel <arstoffel@gmail.com>
- Website
- https://github.com/astoff/jit-spell
- Browse ELPA's repository
- CGit or Gitweb
- Badge
To install this package from Emacs, use package-install or list-packages.
Full description
jit-spell is a spell-checking package for Emacs. It highlights all misspelled words in a window, just like a word processor or web browser does.
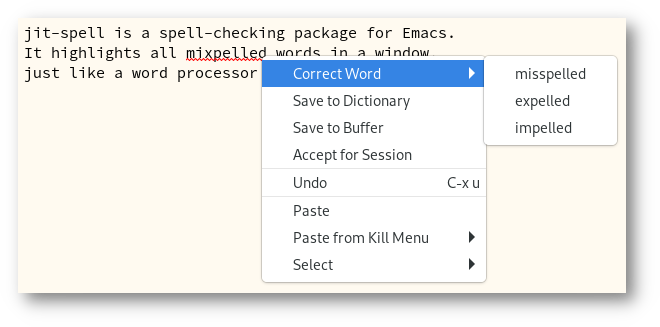
Figure 1: Correcting a misspelling with jit-spell
This behavior is different from the built-in Flyspell package, which only checks words as the cursor moves over them. Moreover, unlike Flyspell, jit-spell communicates with the spell-checking subprocess entirely asynchronously, which can lead to a noticeable performance improvement.
jit-spell is part of GNU ELPA and can be installed with
M-x package-install RET jit-spell RET.
1. Usage
To enable spell checking in a buffer, type M-x jit-spell-mode RET.
To correct a misspelling, you can right-click the word (assuming you
have context-menu-mode activated) or call the command
jit-spell-correct-word, which uses the minibuffer to read a
correction or accept the word.
To make your settings permanent, you may wish to add some variant of the following to your init file:
(add-hook 'text-mode-hook 'jit-spell-mode) (add-hook 'prog-mode-hook 'jit-spell-mode) (with-eval-after-load 'jit-spell (keymap-set jit-spell-mode-map "C-;" 'jit-spell-correct-word))
Try also M-x customize-group RET jit-spell RET to see a listing of
all possible customization options.
Many customization options from the built-in ispell library are also
relevant, notably ispell-program-name. Hunspell and Aspell are the
most common choices. Aspell is faster, but in my experience Hunspell
has better correction suggestions and is sufficiently performant.
2. Language selection
Type M-x jit-spell-change-dictionary RET to choose a different
spelling language. If you use Hunspell, you will be able to select
multiple languages. Other spellchecking programs are limited to a
single language.
The default spellchecking language is determined from your system
settings. To change that, customize the variable ispell-dictionary.
To change the spellchecking language of a specific file, type M-x
add-file-local-variable RET ispell-local-dictionary RET followed by
the desired language (remember to enclose it in quotation marks, since
that variable must be a string). Similarly, you can use
directory-local variables to adjust the spellchecking language for
collections of files.
When using Hunspell, you can set those variables to a comma-separated
list of dictionaries for multi-language spellchecking. See the
explanation of the -d switch in Hunspell's man page for more
information.
3. Major mode support
Often there are regions of the buffer that should be ignored for spell-checking purposes. In most cases, no additional configuration is necessary.
The simplest mechanism to make adjustments is the user option
jit-spell-ignored-faces. Any word fontified with one of these faces
in this list ignored by jit-spell. To find out which faces are
present on a given character, you can use the describe-char command.
In all programming language modes, spell checking is restricted to
comments, docstrings and strings. This can be modified by customizing
the variable jit-spell-prog-mode-faces.
4. Contributing
Discussions, suggestions and code contributions are welcome! Since this package is part of GNU ELPA, contributions require a copyright assignment to the FSF.
Old versions
| jit-spell-0.4.tar.lz | 2024-Mar-31 | 9.27 KiB |
| jit-spell-0.3.tar.lz | 2023-Mar-30 | 8.70 KiB |
| jit-spell-0.2.tar.lz | 2023-Mar-11 | 8.52 KiB |
| jit-spell-0.1.tar.lz | 2023-Mar-05 | 7.55 KiB |